Pulmonary embolism: all you need to know about this respiratory disease
Caution : You must consult your doctor for your health. This page presents only a personal and alternative point of view which should not be considered as an attempt to prescribe medicine.
Pulmonary embolism is a very dangerous special condition for humans.
It has a more or less important mortality and morbidity rate and kills nearly 10,000 people in 100,000 cases.
It is therefore important to know her well to preserve her health.
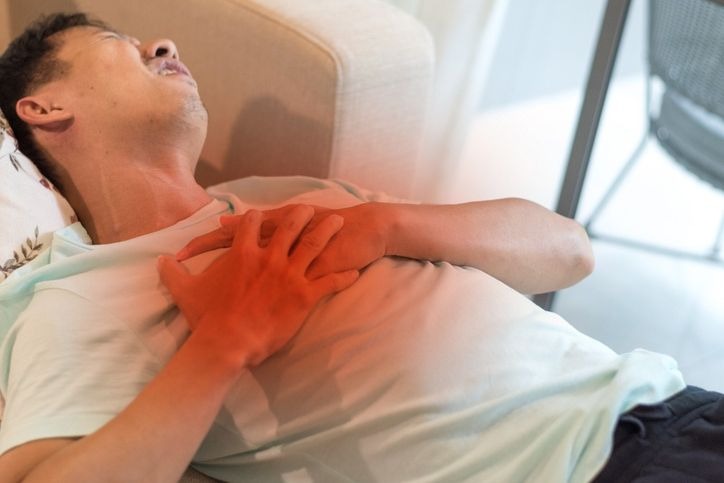
Causes of pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a sudden, partial or total obstruction of one of the arteries supplying the lungs or one of its branches.
This blockage is usually caused by a blood clot that travels to the lungs.
This disease is very dangerous and can occur in anyone, even healthy ones.
However, the elderly and those with cardiovascular diseases are the most at risk.
Pulmonary embolism is usually caused by a blood clot (deep vein thrombosis) forming in a deep vein in a leg, pelvis, or arm.
When this clot does not adhere to the vein poorly, it can break loose and pass through the vascular system into the right heart.
The latter's contractions propel it into the lungs where it blocks the arterial circulation.
However, blood clots are not the only causative agents of pulmonary embolism.
The obstruction of the pulmonary artery may indeed be linked to the presence of:
- fat (during a bone fracture);
- a drop of amniotic fluid (after childbirth);
- tumor cells;
- or an air bubble (decompression sickness during a dive).
These latter causes are occasional, but important to know.
Several situations can favor the formation of blood clots.
A long period of immobilization and bed rest (illnesses, cast immobilizations) or a long period of immobility (long journey for example) are so many occasions which lead to a slowing down of blood circulation.
A clot can then form very easily.
Damage to a blood vessel as a result of muscle damage, bone fractures, or surgery can cause clots to form and aggregate.
Certain pathologies such as cancer can also lead to strong blood clotting.
In addition, age, tobacco and alcohol intake, pregnancy or being overweight are factors, so neglected, which can promote the formation of clots and therefore increase the risk of developing pulmonary embolism.
It is therefore important to note that the part of the lung irrigated by the blocked artery can no longer be supplied with oxygen.
If no action is taken, pulmonary embolism can easily lead to death.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is an often discreet disease with uncharacteristic and not very intense symptoms.
These can vary from person to person depending on the extent of the affected area, the size of the clot and also the patient's condition.
The presence of heart or lung disease can increase the extent of the disease.
Sudden blockage of one or more arteries can manifest itself in a number of ways.
Those affected may experience severe chest pain resembling symptoms of a heart attack.
However, the pain persists despite rest and intensifies even with a deep breath or during a meal.
Pulmonary embolism can also be manifested by difficulty in breathing and sudden, progressive shortness of breath which can occur at rest or during exertion.
The affected person may have a dry cough with release of mucus containing blood.
When the embolism is related to a deep thrombosis, it may be accompanied by pain or redness in the leg.
The condition of pulmonary embolism is quite common.
It is therefore recommended to make a diagnosis as soon as one feels respiratory abnormalities.
Means of combating pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a very dangerous condition.
It is therefore important to take adequate measures as quickly as possible.
Prevention
The best way to reduce the risk of an embolism is to prevent blood clots, especially in the legs.
For this, you must avoid standing still while walking every day.
If you have to sit for a long time, continuously exercise in place.
For long trips, walk and hydrate, if possible, every two hours.
Drink mineralized water, and most importantly, limit alcohol and tobacco consumption.
Anticoagulants and compression stockings are also recommended after surgery to limit the formation of blood clots.
The treatment
The main treatment for embolism is the use of blood thinners.
They limit blood clotting and the formation of clots.
They therefore make it possible to limit the extension of the clot by modifying the composition of the proteins contained in the blood.
In some severe cases, the clots can be removed with medicines called thrombolytics.
In other cases, an embolectomy (surgery) may be necessary.
There are other means of treatment such as the cellar filter for example.
If symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism appear, it is necessary to call your doctor without delay.
Improve your breathing
It is important not to underestimate the power of good breathing in the case of a pulmonary embolism.
Indeed, good breathing could allow better blood circulation and therefore any risk of blockage.
❤ The ultimate guide to breathing
Intermittent Breathing : Discover the method to quickly relieve your anxiety and chronic fatigue (positive effects from the first use).Read also :
Previous article : Difficulty breathing deeply due to stress: what to do?
Next article : Does breathing through the mouth distort the face?

